Honey’s Healthiness Benefits due to its Natural Arrangement and its Types.
Honey’s Healthiness Benefits due to its Natural Arrangement.
Honey is a brown, sticky, sugar-saturated solution produced by bees. Honey bees or forager bees collect nectar from flowers and add some enzymes to the nectar.
“Honey has been revered for its medicinal properties for thousands of years”
Table of Contents
3. Antibacterial and antifungal properties: 1
8. Anti-inflammatory effects: 2
12. Blood Pressor management with honey: 2
13. cholesterol management with honey: 3
How to add honey to cholesterol management 3
Some of the significant polyphenols usually create in honey are: 4
Factors affecting polyphenol content in honey. 4
Health benefits of polyphenols in honey: 4
What happens if we eat honey daily?. 5
What vitamins are in honey?. 5
How much honey is enough per day?. 5
Can I eat honey on an empty stomach?. 5
Here are Some Important Benefits:
Honey contains vitamins, minerals, enzymes and antioxidants. It provides vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and vitamin C, as well as small amounts of minerals such as calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus, potassium, sodium, and zinc.
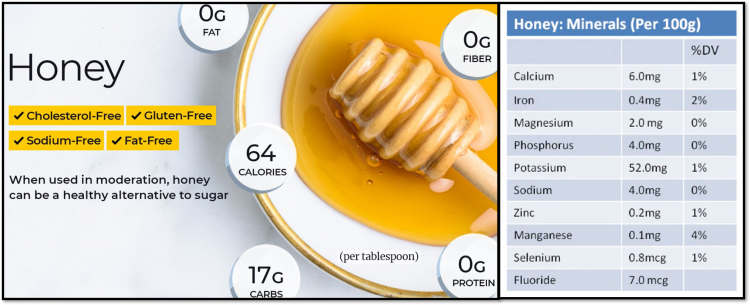
Honey is rich in antioxidants, including phenolic compounds, which help reduce oxidative stress in the body. It can reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.
Due to its low water activity and hydrogen peroxide content, honey has natural antibacterial and antifungal properties. It has been used to treat wounds and burns, promote healing, and prevent infection.
Honey can be an effective cough remedy, especially in children. It helps to soothe the throat and reduce irritation, providing relief from cough.

Honey can promote digestive health by acting as a prebiotic. It helps nourish beneficial gut bacteria, improves gut health and aids digestion.
As a natural source of carbohydrates, honey can provide an instant energy boost. It contains glucose and fructose, which are easily absorbed by the body, making it an excellent source of energy for athletes and active people.

Honey is used in various skin care products due to its moisturizing and antibacterial properties. It can help treat acne, hydrate the skin and improve overall complexion.

Honey has anti-inflammatory properties that help reduce inflammation in the body. It can be beneficial for conditions like arthritis and other inflammatory diseases.

Some people believe that consuming local honey can help reduce allergy symptoms by gradually desensitizing the body to local pollen. However, scientific evidence supporting this claim is limited.

Honey has natural antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties that can promote wound healing. Medical grade honey has been shown to be effective in treating diabetic foot ulcers, burns and other wounds.

Replacing sugar in the diet with honey can help in weight loss. Honey is sweeter than sugar, so less can be used to achieve the same level of sweetness.

Morning routine: Start your day with a glass of warm water with a teaspoon of honey and a few drops of lemon juice.
In tea: Use honey as a natural sweetener in herbal teas, such as green tea or chamomile tea, which have additional health benefits.
With cinnamon: Mix honey with cinnamon, which also has properties that help lower blood pressure. Add a pinch of cinnamon powder to a spoonful of honey and eat it daily.
Smoothies: Add a small amount of honey to your smoothies for extra flavor and health benefits.


Precautions
Quality: Choose raw, unprocessed honey to maximize its health benefits. Managed honey may drop approximately of its useful goods.
Tip: If you have diabetes or another health condition, consult a healthcare professional before adding honey to your diet.
Although honey can help manage blood pressure, it should be part of an overall healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise and stress management.
Honey can also be beneficial for controlling cholesterol levels. Here's how honey can help manage cholesterol:
Antioxidant properties: Antioxidants in honey, such as flavonoids and phenolic acids, can help reduce oxidative stress and prevent oxidation of LDL cholesterol (often called "bad" cholesterol). Oxidized LDL is more likely to form plaque in the arteries, which can lead to heart disease.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Chronic inflammation is a contributing factor in high cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease. The anti-inflammatory properties of honey can help reduce inflammation and, in turn, improve cholesterol levels.
Decreases LDL and increases HDL: Some studies show that honey can help lower LDL cholesterol levels while increasing HDL cholesterol levels (often called "good" cholesterol). This balance is very important for cardiovascular health.
Natural Sweetener: Replacing refined sugar with honey can help control cholesterol levels. Refined sugars and high fructose corn syrup are linked to increased cholesterol levels. Honey, being a natural sweetener with additional health benefits, can be a healthy alternative.
Liver health: Honey can support liver function, and a healthy liver is essential for maintaining balanced cholesterol levels. The liver plays a key role in the production and regulation of cholesterol.

How to add honey to cholesterol management
Honey and lemon water: Start your day with a teaspoon of honey and a few drops of lemon juice in a glass of warm water. It can improve digestion and support liver health.
With Oatmeal: Add a teaspoon of honey to your oatmeal. Oats contain beta-glucan, a type of soluble fiber that can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
In tea: Use honey as a natural sweetener in green tea, which has additional cholesterol-lowering properties.
Honey and cinnamon: Mix honey with cinnamon, which lowers LDL cholesterol levels. Add a pinch of cinnamon powder to a spoonful of honey and eat it daily.
Smoothies: Add honey to your smoothies for natural sweetness and added health benefits.
Although honey can help manage cholesterol, it should be part of an overall healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise and stress management.
Honey is rich in polyphenols, a group of naturally occurring compounds with powerful antioxidant properties. The polyphenol content of honey can vary depending on several factors, including floral source, geographic location and processing methods.
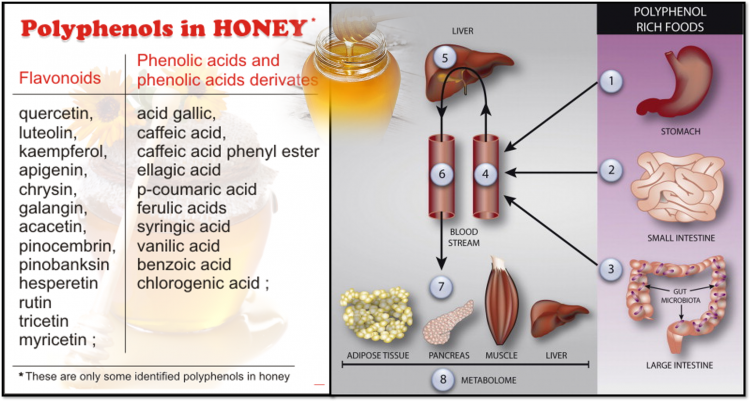
Some of the significant polyphenols usually create in honey are:
Flavonoids: These are the maximum plentiful polyphenols in honey and comprise mixes such as quercetin, kaempferol, apigenin and luteolin. Flavonoids have solid antioxidant and anti-inflammatory chattels.
Phenolic acids: These include mixtures such as caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, and gallic acid. Phenolic acids also contribute to the antioxidant activity of honey and may help protect cells from oxidative damage.
Other polyphenols: Honey may also contain other types of polyphenols, such as stilbenes and tannins, although these are usually present in lower amounts than flavonoids and phenolic acids.
Factors affecting polyphenol content in honey
Floral source: Different types of honey (eg, manuka, buckwheat, acacia) have different polyphenol profiles. For example, Manuka honey is known for its in height levels of methylglyoxal and single polyphenolic compounds.
Geographical location: The area where honey is produced can affect its polyphenol content due to differences in climate, soil and vegetation.
Processing methods: Raw and minimally processed honey generally retain more polyphenols than highly processed honey. Heat and filtration can reduce polyphenol content.
Health benefits of polyphenols in honey:
Antioxidant Activity: Polyphenols help neutralize free radicals, reduce oxidative stress and protect cells from damage.
Anti-inflammatory Effects: Polyphenols can modulate inflammatory pathways, helping to reduce inflammation in the body.
Cardiovascular health: By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation, polyphenols can help improve heart health and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Antibacterial Properties: Certain polyphenols in honey have antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal properties, which contribute to honey's effectiveness in wound healing and infection prevention.
Cancer Prevention: The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of polyphenols may help protect against certain types of cancer by preventing DNA damage and tumor growth.
Maximum number of polyphenols from honey
Choose dark honey: Darker types of honey, such as buckwheat honey, generally contain higher amounts of polyphenols than lighter types.
Choose raw honey: Raw, unprocessed honey retains more polyphenols and other beneficial compounds.
Local and organic honey: Local and organic honey is often less processed and can be higher in polyphenols.

Adding honey to your diet, with its high polyphenol content, can provide numerous health benefits, but should be consumed in moderation due to its natural sugar content.
Types of Honey
Honey comes in various types, each with its own unique flavor, color, and health benefits. Here are some common types of honey and their benefits:
-
Clover Honey
- Flavour: Slight and sweet
- Color: Bright yellowish-brown
- Benefits: Good for restful painful throats and adding sweetness without a solid flavour.

-
Manuka Honey (Famous)
- Flavor: Simple, slightly unpleasant
- Color: Chocolate
- Benefits: Contains high levels of methylglyoxal (MGO), which gives it strong antibacterial properties. Often used for wound healing and boosting the immune system.

-
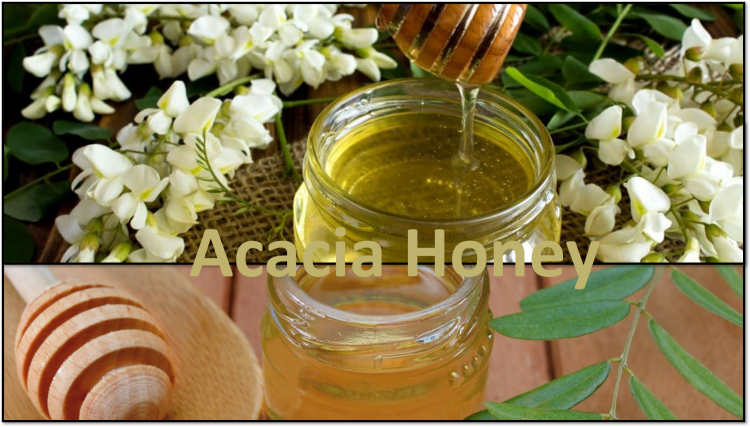
Acacia Honey
- Flavor: Light and flowery
- Color: Very light, nearly transparent
- Benefits: Ironic in antioxidants, known for its gentle taste and slower manifestation.

-
Buckwheat Honey
- Flavor: Strong, molasses-like
- Color: Dark brown
- Benefits: High in antioxidants, good for boosting the immune system and soothing coughs.

1-Eucalyptus Honey
- Flavor: Herbal, slightly medicinal
- Color: Medium to dark amber
- Benefits: Known for its anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties, often used to relieve colds and respiratory issues.

2-Wildflower Honey
- Flavor: Varies depending on the flowers in bloom
- Color: Light to dark amber
- Benefits: Contains a diverse range of antioxidants and nutrients, good for general health and wellness.

3-Orange Blossom Honey
- Flavor: Light and citrusy
- Color: Light amber
- Benefits: Known for its calming properties and rich in antioxidants.

4-Lavender Honey
- Flavor: Floral, slightly herbal
- Color: Light to medium amber
- Benefits: Often used for its calming effects and to promote relaxation.
Note:
It is important to consume honey in moderation due to its high sugar content. Additionally, honey should not be given to kids under one year of age due to the danger of botulism.
Questions & Answers:
What happens if we eat honey daily?
Health benefits of consuming a spoonful of honey daily include diabetes management, cancer management, better heart health and other benefits.
What vitamins are in honey?
According to the US Institute of Health, raw honey contains several vitamins and minerals, including vitamins A, C, D, and E. Honey is especially high in B-complex vitamins, including thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, and pantothenic acid.
Is honey good for skin?
Yes! Honey is a wonderful skin care ingredient. It is known for its antiseptic and antibacterial properties and thus has been used on the skin for centuries. Honey can be used by most people and is especially suitable for sensitive skin and dry skin.
How much honey is enough per day?
The American Heart Association recommends that men eat no more than nine teaspoons (36 grams) per day. Women and children, no more than six teaspoons (24 grams) daily.
Can I eat honey on an empty stomach?
Best time to use: Empty stomach. However, here are some things to avoid when adding honey to your diet: Do not use honey in hot liquids. Do not cook/bake with honey.