OOP CPP Programming language by Nadir Nadeem Part-1
OOP C++ (CPP) Programming language in single view
C++ is a powerful and versatile programming language used to develop a wide variety of software applications, including system software, game development, embedded systems, and more.
Key Features and Features:
Object-oriented: C++ supports object-oriented programming (OOP) paradigms, including classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation.
High performance: C++ is known for its high performance and efficiency, which makes it suitable for resource-intensive applications and system programming.
Compiled Language: C++ is a compiled language.
Platform independence: C++ code can be compiled to run on different platforms, including Windows, Linux, MacOS, etc.
Standard Library: C++ provides a rich standard library (STL) that includes data structures, algorithms, input/output operations, and utilities.
Memory Management: C++ offers manual memory management through pointers as well as automatic memory management through features like smart pointers and RAII (Resource Acquisition Is Initialization).
Low-level control: C++ allows low-level memory manipulation and direct hardware access, giving developers precise control over system resources.
Templates: C++ templates enable generic programming, allowing functions and classes.
Multi-paradigm: C++ supports multiple programming paradigms, including procedural, object-oriented and generic programming.
Overall
C++ is a flexible and powerful language with a wide range of applications, offering developers the tools they need to create efficient, scalable, and high-performance software solutions.
Lab Work:
C++ Programming with example:
C/C++ Language:
Software requirement:
 DevC++
DevC++
Download Link:
Table of Contents
Color List (Standard console 16 color values) 14
Language:
- Communication way is called language.
- Language must be same from both side
- If not same è solution is translator
Translator:
- Convert from one language to another language
Translator Types:
- Line by line (Interpreter)
- Read whole program and then give the result (Compiler)
Language types:
- Low-level languages (special purpose)
- For example:
- Machine language
- Assembly language
- Program (Apps)
- Operating system
- Virus
- Anti-virus
- Drivers
- Program (Apps)
- For example:
- Hegh-level Language (common purpose languages)
- c/cpp
- Java
- Python
- Java script
- HTML
- PHP
- etc. etc.
Language have:
- Alphabets: a single alphabet is called letter. è Char (Character)
- Word: set of chars is called word. è Keyword or Reserve word
- Statement: set of words is called statement. è conditions and loop
- Paragraph: set of statements is called paragraphè function/method
- but in true sequence:
Set of chars word but in true sequence:
- Sleep
Selep
He is going to school.
He to going is school.
Lecture-2
Cpp Application:
- Run DEVc++ IDE
Interface:
IDE (Editor) è Integrated Development Environment

C/Cpp Language tips:
- End statement with Sami colon è;
- Freeze any line è // binging of line or statementà ctrl+/
- Every block start with { and end with }
- Ext of c++ è.cpp
CPP program structure
- A program structure must be written every time a new program is created.
|
#include<iostream> using namespace std; int main(...) { Coding area Return 0; } |
Programming in c/c++
Create a new program(project)
File à New à Project à select console à write project name
Output/input functions
1:- output function
- cout<<
Syntax: (method of writing)
cout<<”Any text”;
|
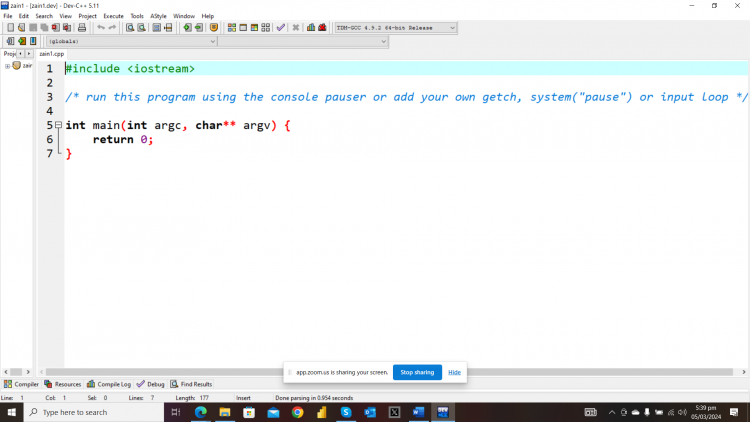
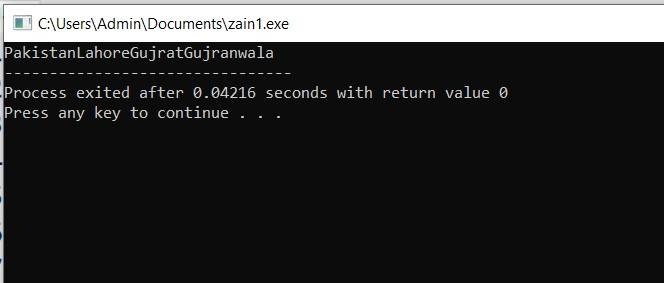
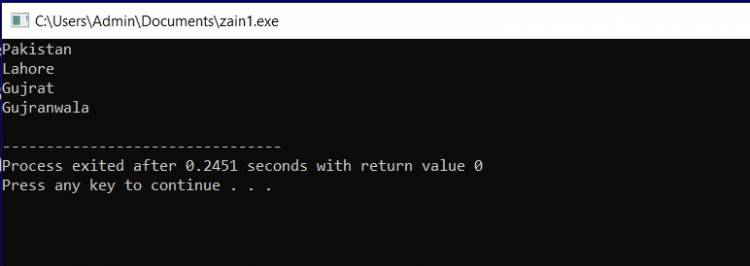
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { cout<<"Pakistan"; cout<<"Lahore"; cout<<"Gujrat"; cout<<"Gujranwala";
return 0; } |
Output:
|
Example: with endl #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { cout<<"Pakistan"<<endl; cout<<"Lahore"<<endl; cout<<"Gujrat"<<endl; cout<<"Gujranwala"<<endl;
return 0; } |
Output:
For new line
- endl
- \n
|
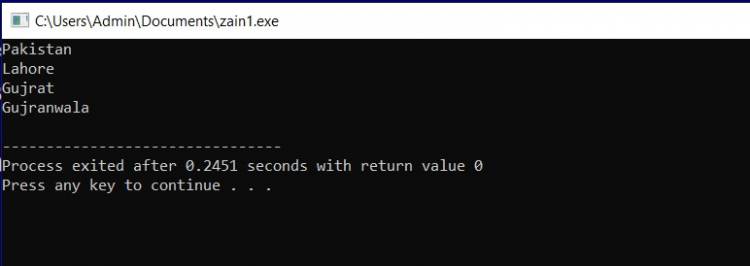
Example: with \n (Escape sequence) #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { cout<<"Pakistan\n"; cout<<"Lahore\n"; cout<<"Gujrat\n"; cout<<"Gujranwala\n";
return 0; } |
Output
Escape sequence:
- \nè new line
- \t è tab
- \b è back space
- \” è print double quotes
- \\ è print back slash
- Etc
==================================
Assignment 1: My complete Biodata
==================================
Name: Ali
F_Name: ….
City
Address
Cellno
=======================
Composed by apna apna name
|
Example: assignment hint #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { cout<<"========================"<<endl; cout<<" Maaz\\Ali"<<endl; cout<<"========================"<<endl; cout<<"Name: Ali"<<endl; return 0; } |
Lecture-3:
- cout<<”text”;
- cout<<numaricvalue;
- cout<<variable;
|
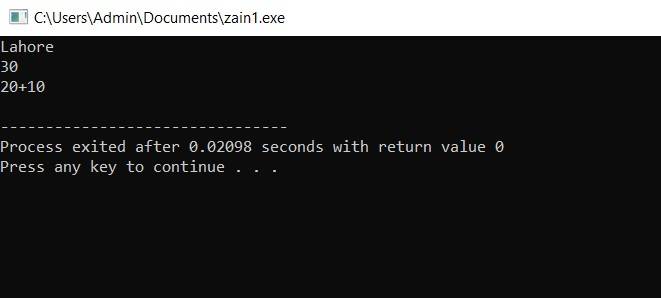
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) {
cout<<"Lahore"<<endl; cout<<20+10<<endl; cout<<"20+10"<<endl; return 0; } |
Output
Operators:
- Arithmetic operators
- + è sum
- – è subtraction
- *è multiplication
- / è division
- % è remainder (Mod) Modulo
- = è equal to (assignment operator)
- Comparison operators
- <
- >
- <=
- >=
- !=
- ==
- Logical operators
- And è&&
- Or è||
- Not è!
- Increment operators
- ++ è single increment
- += è multiple increment
- Decrement operators
- - -
- -=
Variable:
- Global variable (public)
- Local variable (private)
x=10
X è is called variable
10 è value of x
Data type commonly:
- Alphabetic data (text data or string)
- Numeric data
- Alphanumeric data
- MM data
- Image
- Video
- Audio
Datatype in cpp:
- Numeric data type:
- int è for integer value
- float è floating point value
- double è floating point value
- Text data types
- string
- char
Variable declaration:
Syntax:
- datatype variable;
- datatype variable=value;
ie.
int x=10;
|
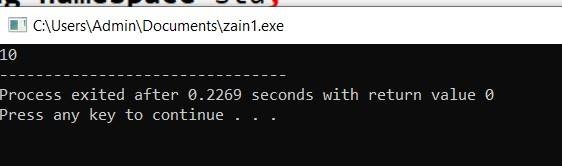
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x=10; cout<<x; return 0; } |
Output
Variable rules :
X, x1, y2, sum, sum_2, abc_v1… è true
1x, sum-1, sum w, … è false
|
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x=10; float y=20.8; string s1="Pakistan"; cout<<x<<endl; cout<<y<<endl; cout<<s1<<endl; return 0; } |
Output:
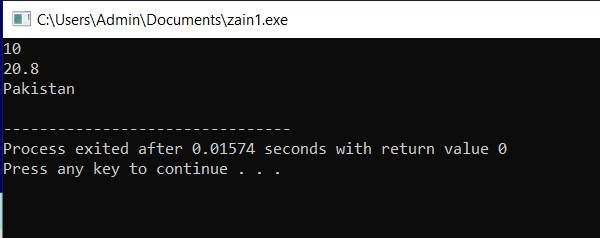
|
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x=10; float y=20.8; string s1="Pakistan"; cout<<"Value of x= "<<x<<endl; cout<<"Value of y= "<<y<<endl; return 0; } |
Output
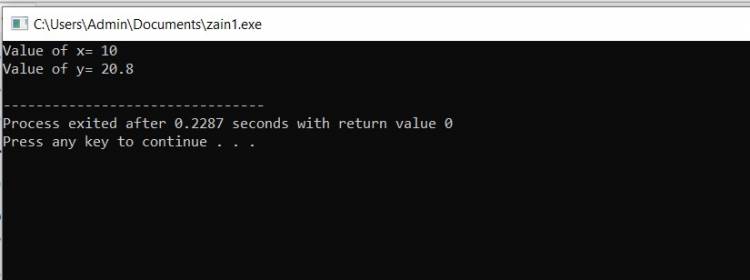
|
Example: #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x=10,y=5; // x=10; // y=5; cout<<"1st value:= "<<x<<endl; cout<<"2nd value:= "<<y<<endl; cout<<"Sum of both values:= "<<(x+y)<<endl; cout<<"Sub of both values:= "<<(x-y)<<endl; cout<<"Mul of both values:= "<<(x*y)<<endl; cout<<"Div of both values:= "<<(x/y)<<endl; cout<<"Mod of both values:= "<<(x%y)<<endl;
return 0; } |
Output:
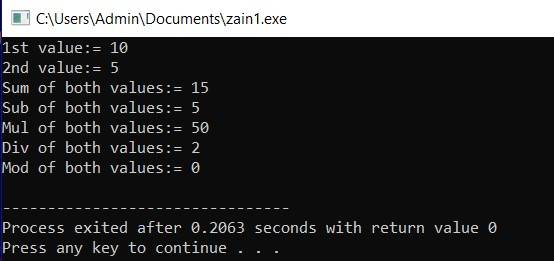
Lecture-4:
Input function:
cin>>
- syntax:
- cin>>variable;
|
example: with input function cin>> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x; cout<<"Enter int value:= "; cin>>x; cout<<"Your entered value:= "<<x<<endl;
return 0; } |
Output
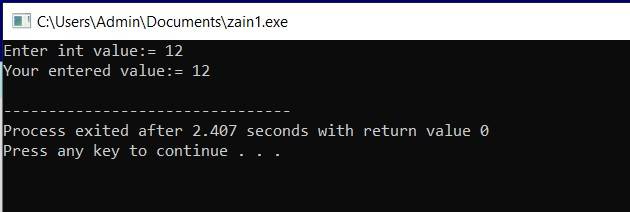
Ass#2: Simple calculation
Enter 1st value:= 10
Enter 2nd value:= 5
1st value:= 10
2nd value:= 5
Sum of both = 15
Sub of both = 5
Mul of both = 50
Division of both = 2
Mod value= 0
Color in CPP console:
Function (System()):
- System()
- syntax(“Color bf”);
- b àbackground color value
- fàforeground color value
- syntax(“Color bf”);
Library name:
- <windows.h> OR <stdlib.h>
Color List (Standard console 16 color values)
|
Color id |
Color |
Color id |
Color |
|
1 |
Blue |
9 |
Light Blue |
|
2 |
Green |
0 |
Black |
|
3 |
Aqua |
A |
Light Green |
|
4 |
Red |
B |
Light Aqua |
|
5 |
Purple |
C |
Light Red |
|
6 |
Yellow |
D |
Light Purple |
|
7 |
White |
E |
Light Yellow |
|
8 |
Gray |
F |
Bright White |
Example:#include <iostream> #include <windows.h> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { system("Color 04"); cout<<"Ahmed Raza"<<endl; return 0; } |
Output:
Color with
- SetConsoleTextAttribute() function &
- GetStdHandle() function with STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE object
- Syntax:
- SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),color_value);
|
Example: #include <windows.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),4); cout << "Using colour:"<<endl; SetConsoleTextAttribute(GetStdHandle(STD_OUTPUT_HANDLE),18); cout << "Using colour:"<<endl;
} |
Input functionè Assignments
Ass#3 calculate area of rectangle: (L*W):
Enter length of rec:= 2
Enter width of rec:= 3
Length =2
Width = 3
Area of rectangle:= 6
Ass#4 calculate area of circle: (pi*r*r):
Enter radius of circle:= 6
6 radius have area of circle is ….
Ass#5 calculate area of triangle: (1/2*l*w)
Ass#6 Convert KM to Meters & Meters to KM
Enter KM: 6
6 KM = 6000 Meters
Ass#7 Convert Cg to Fh & fh to c0
Ass#8 Convert KG to Gram & Gram to KG
Lecture 5
Conditional statements:
- If- else (single condition)
- If- else if -else (multiple conditions)
- Switch-case (multiple conditions)
1:- if-else
Syntax:
If(condition){
Blok1
}
else{
block2(default block)
}
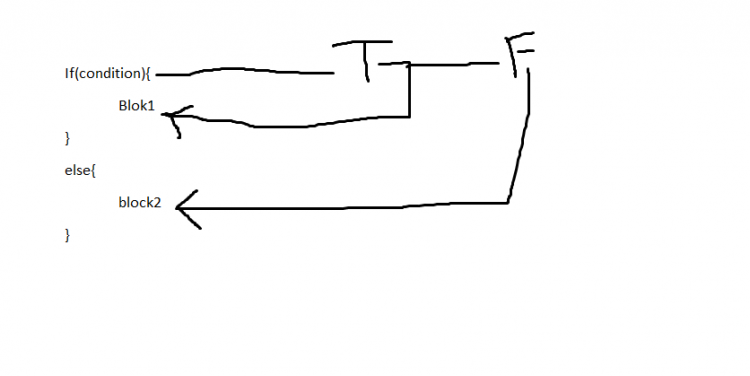
|
Example: #include <iostream> #include <windows.h> using namespace std; int main(int argc, char** argv) { int x=10; if(x>100){ cout<<"Ahmed"; } else{ cout<<"Danial"; }
return 0; } |
Output