Topical Authority means and content clusters mean
Topical authority means what content clusters mean.
Absolutely! Below is a detailed and extensive guide to the concept of topical authority and content clusters, a cornerstone of modern SEO and content strategy in 2025:
Table of Contents
Topical authority means what content clusters mean. 1
1. Pillar Content (Main Page): 3
2. Cluster Content (Supporting Pages): 3
How Google Uses Topical Authority (2025 Algorithm Insights) 3
How Google Uses Topical Authority in 2025. 3
Key Points for Content Strategy in 2025. 5
Topical Authority and the Benefits of Clustering. 5
How is Topical Authority Created?. 5
???? What is content clustering?. 6
Benefits of Clustering for Topical Authority. 6
Visual representation of topic clusters. 7
1. Pillar Page (Central Node) 7
???? 2. Topic Clusters (Probing Nodes) 7
???? 3. Internal Linking (Connected Lines) 7
Tools for Creating Cluster Maps. 8
5. SEO Ranking Content Marketing Tool 8
Template (Manual Planning) – Google Sheets / Excel 8
How to create content clusters for topical authority. 9
Step 1: Choose a basic topic. 9
Step 2: Research keywords and intent. 9
Step 3: Create a pillar page. 9
Step 4: Write clustered articles. 9
Tools to help you create clusters. 10
What is a topical authority?. 11
What is topical clustering in SEO?. 11
What are the three types of clustering?. 11
What is Topical Authority?
Topical authority is the depth and breadth of expertise a website demonstrates around a specific topic area.
Instead of ranking based solely on individual keywords, Google now prefers websites that demonstrate comprehensive coverage of a particular topic. To wit:
"The more quality, interconnected content you produce on a particular topic, the more likely search engines will consider you a trustworthy expert in that area."
Example:
If you have a health blog, you won't gain authority just by writing a post titled "How to Lose Weight." You'll need:
- Posts on calorie intake, exercise routines, diet types, the science of metabolism, eating plans, etc.
- Internal connections between them
- Consistency and depth of topic.
________________________________________________
What are content clusters?
Content groups (also known as topic clusters) are a systematic way to build topical authority by organizing blog content around core topics.
Structure:
1. Pillar Content (Main Page):
- A comprehensive, long-form post that covers a major topic in general.
- For example, "The Ultimate Guide to Digital Marketing"
2. Cluster Content (Supporting Pages):
- More in-depth articles that break down specific subtopics.
- For example, "Email Marketing Strategy," "SEO for Beginners," "Guide to Social Media Ads"
3. Internal Links:
- All articles in the cluster link to the pillar post, and vice versa.
This tells Google, "These pages are part of a larger, authoritative work."
________________________________________________
How Google Uses Topical Authority (2025 Algorithm Insights)
Google Now:
- Analyzes site structure to determine if you're a journalist or an expert.
- Uses semantic search and natural language processing (NLP) to understand topical relationships.
- Prefers sites that satisfy user intent on all angles of a topic, not just one.
Sites that consistently follow up and answer relevant questions are more likely to rank higher and have featured snippets.
More…
By 2025, Google's use of topical authority will have become more sophisticated and central to its ranking algorithm, especially in the context of E-E-A-T (Expertise, Knowledge, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). Here's a detailed look at how Google leverages topical authority and what it means for content creators and SEO professionals.
How Google Uses Topical Authority in 2025
1. Entity Understanding and Semantic Relevance
- Google now maps entities (people, places, topics) and relationships between topics using AI-powered language models.
- This assesses whether your site demonstrates depth and breadth of coverage around a specific topic group.
- Example: A health site with more than 50 interconnected and detailed pages on gut health (probiotics, prebiotics, microbiome research) creates stronger topical authority than one with scattered, unrelated health articles.
2. Information Acquisition Scores
- Google increasingly values originality and freshness in content.
- If your article provides new knowledge or explains the topic better than existing pages, it will likely get a higher score.
- Duplicate or lower-quality content, even if keyword-specific, loses visibility.
3. Structured and Context-Sensitive Content Architecture
- Strong internal connections between related materials indicate the focus and authority of explicit situations.
- Well-organized topic clusters (pillars + subtopics) now receive greater rewards in the hierarchy.
- Google's crawling and indexing system recognizes semantic proximity between linked pages.
4. Authority Signals
- With the rise of authorship recognition (linked to Google's AI-powered entity understanding), content written by recognized experts carries more weight.
- This includes:
- Author bio with credentials
- Linked author profiles (via structured data)
- Historical web posting behavior
5. User interaction and engagement signals
- Google uses behavioral data to verify authority:
- Time on page
- Click-through rate (CTR)
- Scroll depth
- Return visits
- Compelling, well-structured content that answers user questions well, enhances those signals, and reinforces the credibility of the situation.
6. Extraneous personalization was preferred over generalization.
- Specific sites that delve into a specific vertical (e.g., "herbal skincare" instead of "beauty") outperform broader sites without a clear focus.
Key Points for Content Strategy in 2025
Why is this strategy important?
- Creating comprehensive clusters improves semantic coverage and internal linking.
- Demonstrate real-world expertise supporting E-E-A-T; it increases author and brand trust.
- Optimize for user intent. Google understands deeper intent, not just keywords.
- Keeping content fresh and achieving unique information scores is important.
- Using structured data helps Google Maps with entities, authors, and titles.
Pro Tip:
Do you want your SEO to be future-proof?
Choose a niche, dig deeper, and create a semantic map of related content. Write like a human, structure like a pro, and demonstrate real-world skills.
________________________________________________
Topical Authority and the Benefits of Clustering
Topical authority and content clustering are fundamental concepts in modern SEO and content strategy. Let's break them down and discover how they work together to improve search engine rankings, generate organic traffic, and position a website as a trustworthy source.
What is Topical Authority?
Topical authority refers to how much credibility and expertise a website (or author) has on a specific topic in the eyes of a search engine like Google.
Think of it this way:
- A site with Topical Authority on "vegan nutrition" has extensive, high-quality, and interconnected content on vegan diets, recipes, health tips, common deficiencies, supplements, and more.
- Google sees this depth and breadth as a sign that the site is a trustworthy source.
How is Topical Authority Created?
- Publish comprehensive content on a topic
- Demonstrate expertise (through depth, references, and E-E-A-T signals)
- Earn backlinks from other authoritative sites in the same niche
- Keep content fresh and up-to-date
- Creating content with clusters (more on this later)
???? What is content clustering?
Content clustering is a way to organize your website's content around core themes or topics. The idea is to create a "pillar" page that provides a broad overview of a topic and then support it with "cluster" content that delves deeper into subtopics.
Example:
Main Topic: "Digital Marketing Strategy"
Clusters:
- Email Marketing Best Practices
- SEO for Beginners
- Social Media Campaigns
- PPC vs. Organic Traffic
- Digital Marketing Tools
Each page in the cluster links to the pillar (and vice versa), creating a strong internal linking structure.
Benefits of Clustering for Topical Authority
- Better SEO and Rankings
- Interconnected content shows Google that you cover the topic thoroughly.
- Increases keyword coverage (broad and long tail)
- Better user experience
- Visitors can easily navigate to relevant content.
- Reduces bounce rate and increases time on site.
- High topical relevance
- Helps Google understand what your site is about.
- You're more likely to rank well for a variety of search queries within the same topic.
- Supports E-E-A-T (Expertise, Knowledge, Authority, Trustworthiness)
- Especially important for YMYL (Your Money or Your Life) topics
- Simple content planning
- Helps structure your editorial calendar.
Ensures you're covering all relevant angles of a topic.
Putting it all together
To become an authority on your topic, you need:
- Deep and interconnected content (clusters)
- Well-thought-out internal links
- Consistency and skill
- Clear focus on user intent
A well-planned content cluster strategy is one of the fastest and most sustainable ways to build this authority over time.
________________________________________________
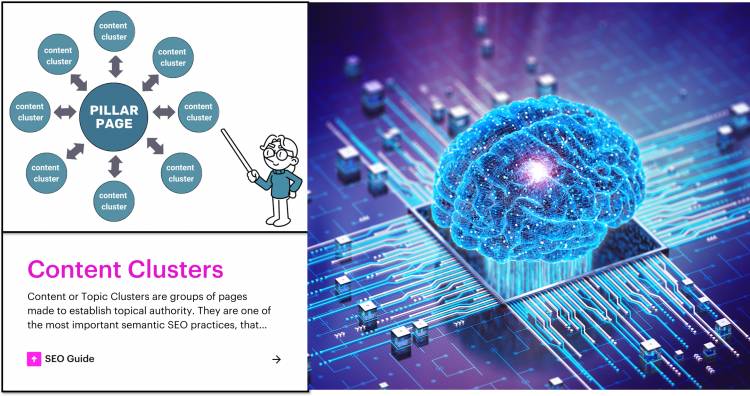
Visual representation of topic clusters
A visual representation of topic clusters is a diagram that shows how content links around a central topic ("pillar page") with related subtopics ("cluster content"). This model is key in SEO and content strategy.
Below is a breakdown of each element of the diagram:
1. Pillar Page (Central Node)
- Definition: A main content page that broadly covers a central topic.
- Purpose: Serves as an authority page on a topic and serves as a hub for related content.
- Material Properties:
- Coverages the topic comprehensively but generally.
- Typically, long content (e.g., the ultimate guide)
- Links to cluster pages
???? 2. Topic Clusters (Probing Nodes)
- Definition: Subheadings that relate to and expand on the main topic.
- Goal: To delve deeper into specific aspects of the central pillar topic.
- Material Properties:
- More specific and niche articles or posts
- Link to the pillar page (and sometimes to each other)
- Target long-tail keywords
???? 3. Internal Linking (Connected Lines)
- Definition: Hyperlinks between pillar and cluster content.
- Purpose:
- Improves site navigation and SEO.
- Helps Google understand the relationship between pages.
- Conveys authority and relevance between related pages.
- Example in Context
- Imagine your website is about digital marketing.
- Home Page: "The Ultimate Guide to Digital Marketing"
- Clusters:
- What is SEO and why is it important?
- "Social Media Marketing Strategy"
- Email Marketing Tips for Beginners
- Google Ads vs. Facebook Ads
- How to Track Marketing KPIs
Each article in the cluster is closely related to the main topic and connected to the pillar. The pillars, in turn, connect to each cluster, creating a content ecosystem.
Benefits of Visual Models
- Easy to understand: Visually shows the content structure.
- SEO-friendly: Demonstrates logical internal links.
- Content holes: Helps find missing subheadings.
- Planning tool: Guides editorial strategy.
Tools for Creating Cluster Maps
1. Lucid chart (web-based)
Use: Create flowcharts, diagrams, and topic clusters.
Features: Drag-and-drop interface, templates, export options, team collaboration.
Best for: Visually mapping complex content strategies.
2. I see.
- Use: Digital whiteboard for mind mapping and planning.
- Features: Templates for SEO topic clustering, sticky notes, collaboration.
- Best for: Team brainstorming and visual mapping.
3. Mind master
- Use: The mind mapping tool is ideal for content and topic trees.
- Features: Easy branching structure, PDF/Word exports.
- Best for: Individual creators planning a visual tree-like design.
4. Concept
- Use: All-in-one workspace with database and linked pages.
- Features: Manually create internal links between pillars and cluster notes.
- Best for: Content managers who prefer structural planning to visual maps.
5. SEO Ranking Content Marketing Tool
- Use: Create topic plans based on clustered keyword research and search intent.
- Best for: SEO-focused content grouping and competitive analysis.
Template (Manual Planning) – Google Sheets / Excel
You can use a simple table structure like this:
- Pillar Topic Cluster Topic Target Keyword URL Slug Status
- Social Media Digital Marketing Strategy Social Media Tips / Published Social Media
- Digital Marketing Email Marketing Guide / Email Marketing Draft
- SEO Basics for Digital Marketing was published in SEO for Beginners / seo-basics.
Use it as an editorial calendar or map to track networking opportunities.
________________________________________________
How to create content clusters for topical authority
Step 1: Choose a basic topic.
- It should be relevant to your niche, have a high search volume, and align with your expertise.
- Examples: “Personal Finance,” “Plant-Based Diet,” “AI in Marketing”
Step 2: Research keywords and intent.
Use tools like:
Alphabets
- Semirsh
- Google People Also Ask.
- Provide a public answer.
Break the main topic into subtopics, questions, and search intent (informational, transactional, navigational).
Step 3: Create a pillar page
- Cover the main topic in 2,000 to 3,000 words.
- Use H1/H2/H3 structure, rich media, and internal links.
- Think of it as a “hub” page for a topic.
Step 4: Write clustered articles.
- Focus each article on a subheading or long-tail keyword.
- Answer specific questions
- and users.
- Keep articles between 800 and 1,500 words.
- Link to the main post.
Step 5: Connect everything.
- Use clear anchor text (e.g., "Learn more in our on-page SEO guide")
- Pillar link ↔ cluster ↔ other clusters.
Ensure crawlability and a logical site structure.
Step 6: Update regularly.
- Keep statistics, tools, and references up to date.
- Add new cluster pages as your site evolves.
- Real-Life Example: Travel Blog
- Pillar: "The Complete Guide to Traveling in Europe"
Cluster Topics:
- "The Best Low-Cost Airlines in Europe"
- "The 10 Best Cities for Slow Travelers"
- "Train vs. Plane: How to Get Around Europe"
- "Visa Requirements for American Travelers"
- "Packing List for a European Summer"
All of these links back to the main guide and to each other when relevant.
________________________________________________
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Why does this mistake hurt?
- Simply writing random, standalone posts with no internal structure = no discernible skill.
- Targeting broad, high-competition keywords is simply hard to rank for and fails to cover the entire topic.
- Weak internal links result in missed SEO signals and poor user navigation.
- Thin content doesn't satisfy searcher intent or build authority.
- Ignoring user queries resulted in the loss of long-tail traffic opportunities and snippets.
________________________________________________
Tools to help you create clusters
Objective tools
- Keyword research: Ahrefs, SEMrush, Ubersuggest, Keyword Chef
- Cluster planning: SurferSEO, Frase, MarketMuse
- Internal linking: Link Whisper (WordPress), Screaming Frog
- Content roundup: Jasper, ChatGPT, Content Sync.
- Also requested: SERP analysis, Google PAA, SEO minion
________________________________________________
Final thoughts
Topical authority and content clusters are no longer just trendy tactics: they are fundamental SEO strategies in 2025.
If your goal is to achieve high rankings, build trust, and generate sustainable traffic, creating structured, interconnected, and in-depth content on specific topics is non-negotiable.
Q/A
What is a topical authority?
It's about attractive a righthand basis of info on a specific subject.
What is topical clustering in SEO?
Topical clusters(collections) are an SEO strategy where a vital "pillar" page is linked to several related "cluster" pages.
What are the three types of clustering?
Cluster Types:
- Centroid-based clustering.
- Density-based clustering.
- Distribution-based clustering.
- Hierarchical clustering.