Edge Computing: Exploring the Potential of Edge Computing
Edge Computing
Edge computing is a distributed computing model that brings computation and data storage closer to the sources of data. This is likely to improve response times and save bandwidth. Edge computing is an architecture rather than a specific technology, and a topology- and location-sensitive form of distributed computing.
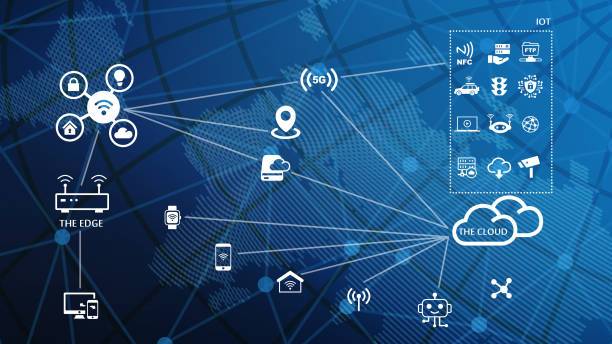
The main difference between edge computing and cloud computing is that edge computing brings the computing resources closer to the data, while cloud computing keeps them in a centralized location. This makes edge computing ideal for applications that require low latency, such as real-time video streaming or autonomous vehicles.
Here are some of the benefits of edge computing:
- Reduced latency: Edge computing can significantly reduce latency by bringing the computing resources closer to the data. This is important for applications that require real-time response, such as self-driving cars or medical devices.
- Improved bandwidth utilization: Edge computing can help to improve bandwidth utilization by processing data locally. This can be especially beneficial in areas with limited bandwidth, such as rural areas or developing countries.
- Increased security: Edge computing can help to improve security by reducing the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network. This can make it more difficult for hackers to intercept or steal data.
- Enhanced privacy: Edge computing can help to enhance privacy by processing data locally. This can reduce the amount of data that needs to be shared with third parties.
Challenges of edge computing:
- Complexity: Edge computing can be more complex to manage than cloud computing. This is because there are multiple edge devices that need to be coordinated.
- Cost: Edge computing can be more expensive than cloud computing, especially for small businesses.
- Security: Edge devices can be more vulnerable to security attacks than cloud servers.
- Regulation: Edge computing may need to comply with different regulations depending on the location of the edge devices.
Overall, edge computing is a promising new technology that can offer many benefits for businesses and organizations. However, it is important to weigh the benefits and challenges before deploying edge computing.
Examples of edge computing:
- Smart cities: Edge computing can be used to collect and process data from sensors in smart cities, such as traffic cameras and environmental sensors. This data can be used to improve traffic management, optimize energy use, and improve public safety.
- Autonomous vehicles: Edge computing can be used to process data from sensors in autonomous vehicles, such as cameras and radar. This data can be used to help vehicles navigate safely and avoid obstacles.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Edge computing can be used to collect and process data from IoT devices, such as wearables and industrial sensors. This data can be used to monitor and control devices and to gain insights into operations.
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): Edge computing can be used to deliver VR and AR experiences with low latency. This is important for applications such as gaming and training.
More features and concepts of edge computing include:
Low Latency: By processing data closer to its source, edge computing reduces the time it takes for data to travel back and forth between devices and distant data centers. This is critical for applications requiring real-time responsiveness, such as autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and augmented reality.
Bandwidth Efficiency: Transmitting large amounts of data to centralized data centers can strain network bandwidth. Edge computing helps alleviate this issue by filtering and processing data locally, sending only relevant information to the cloud. This can lead to significant savings in terms of bandwidth costs.
Privacy and Security: Edge computing can enhance data privacy and security by keeping sensitive information localized and minimizing the exposure of data to external networks. This is especially important in applications dealing with sensitive data, like healthcare and finance.
Offline Operation: Edge devices can continue to function even when disconnected from the cloud, allowing them to operate in environments with limited or intermittent connectivity. This is beneficial for applications that require uninterrupted operation.
Scalability: Edge computing can distribute computational load across numerous edge devices, improving scalability for applications that might otherwise overwhelm a centralized data center.
Real-time Analytics: Processing data at the edge allows for immediate analysis and decision-making based on local insights. This is particularly valuable for scenarios where rapid response is crucial.
Variety of Devices: Edge computing can be implemented on various types of devices, ranging from IoT sensors and gateways to routers and more powerful edge servers.
Challenges: Despite its benefits, edge computing also presents challenges, such as managing a large number of edge devices, maintaining consistency across distributed systems, and dealing with potential hardware and software constraints on edge devices.
Edge computing finds applications in a wide range of industries, including “manufacturing, healthcare, transportation, agriculture, and smart cities.” It complements cloud computing by extending the capabilities of the network and enabling more efficient and responsive data processing.
A Short Overview of Edge Computing:
Key Points:
- Edge Computing
- Distributed Computing
- Real-time Processing
- Low Latency
- Bandwidth Efficiency
- Data Privacy
- Data Security
- IoT (Internet of Things)
- Cloud Computing
- Scalability
- Real-time Analytics
- Internet Infrastructure
- Edge Devices
- Industry 4.0
- Smart Cities
- Industrial Automation
- Data Localization
- Network Efficiency
- Data Processing Paradigm
- Decentralized Computing




























Ali Shah
Informative very naice