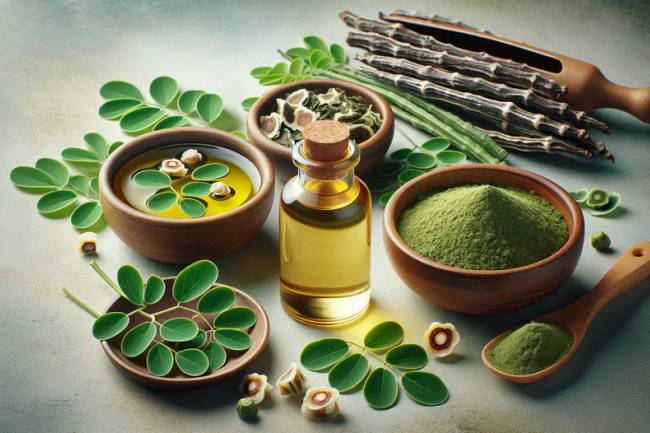
Adaptogens (a natural substance considered to help the body adapt to stress)
Adaptogens(a natural substance considered to help the body adapt to stress)
Adaptogens are natural substances, usually herbs and mushrooms, that are thought to help the body resist physical, chemical, or biological stressors. They have been used in traditional medicine, particularly Ayurveda and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM), for centuries to promote balance, increase energy, and improve stress resistance. Below is a detailed breakdown of adaptogens, their types, benefits, and mechanisms.
Table of Contents
1. Definition and Procedure. 1
2. Common Adaptogenic Herbs and Mushrooms. 1
A. Ashwagandha (Vythenia somnifera): 1
C. Holy Basil (Ocimum santa or Basil): 2
D. Ginseng (Panax ginseng and Eleutherococcus senticosus): 2
E. Cordyceps (Cordyceps sinensis): 2
F. Schisandra (Schisandra chinensis): 2
G. Licorice Root (Glyceriza glabra): 2
3. Key Benefits of Adaptogens. 3
1. Definition and Procedure
Adaptogens work primarily by regulating the body's response to stress. Stress, whether physical (e.g., exercise), mental (e.g., work stress), or environmental (e.g., pollution), can activate the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which releases stress hormones such as cortisol. Adaptogens are thought to help balance these hormones and prevent the HPA axis from overreacting, thereby maintaining homeostasis (balance).
They generally act in a non-specific manner, meaning they help the body adapt to different types of stress without targeting a specific condition. Unlike stimulants, which boost energy by tapping into reserve energy, adaptogens focus on how the body responds to stress to boost energy.
2. Common Adaptogenic Herbs and Mushrooms
About well-known adaptogens, their sources, and potential benefits:
A. Ashwagandha (Vythenia somnifera):
- Origin: Ayurveda (India).
- Key Benefits: Reduces anxiety, lowers cortisol levels, increases stamina, improves cognitive function, and improves sleep.
- How it Works: Ashwagandha is known to modulate the stress response and have calming effects that may combat anxiety.
B. Pink Rhodiola:
- Origin: Traditional Siberian and Scandinavian medicine.
- Key Benefits: Reduces fatigue, improves mental performance, increases stamina, and helps stabilize mood.
- How it works: Rhodiola is thought to improve the body's resistance to stress by reducing cortisol levels and improving nervous system function.
C. Holy Basil (Ocimum santa or Basil):
- Origin: Ayurveda (India).
- Key Benefits: Anti-inflammatory, boosts immune function, balances blood sugar, and reduces stress-related anxiety.
- How it works: Basil is thought to help reduce physical and emotional stress by stabilizing the HPA axis and boosting overall immune function.
D. Ginseng (Panax ginseng and Eleutherococcus senticosus):
- Origin: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
- Key Benefits: Increases energy levels, improves cognitive function, enhances physical performance, and supports immune function.
- How It Works: Ginseng helps regulate the body's response to stress by affecting the adrenal glands and HPA axis.
E. Cordyceps (Cordyceps sinensis):
- Origin: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
- Key Benefits: Increases athletic performance, improves endurance, supports respiratory health, and increases energy levels.
- How It Works: Cordyceps are mushrooms that increase the body's production of ATP, an energy molecule, which helps improve oxygen utilization and physical performance.
F. Schisandra (Schisandra chinensis):
- Origin: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
- Key Benefits: Supports liver health, increases mental clarity, boosts stamina, and balances mood.
- How it works: Schisandra berries are known for their ability to support the adrenal glands, balance stress hormones, and improve focus.
G. Licorice Root (Glyceriza glabra):
- Origin: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
- Key Benefits: Supports adrenal function, reduces fatigue, and balances blood sugar levels.
- How it works: Licorice root helps maintain cortisol levels and increases the half-life of cortisol in the body, which can boost energy in stressful situations.
3. Key Benefits of Adaptogens
- Stress Reduction: Adaptogens help balance the production of stress hormones, especially cortisol, and regulate the body’s response to stress.
- Energy and Endurance: Unlike caffeine or other stimulants, adaptogens support sustained energy by improving the body’s resistance to stress and supporting metabolic processes.
- Cognitive Function: Certain adaptogens (such as rhodiola and ashwagandha) are known to improve focus, memory, and mental clarity, especially under stress.
- Immune Support: Many adaptogens have immune-enhancing properties, supporting the body’s ability to fight off infections and recover from illness.
- Hormonal Balance: Adaptogens such as ashwagandha and holy basil help balance hormones, which can be especially beneficial for those experiencing hormonal fluctuations due to stress or aging.
- Anti-Aging and Longevity: Many adaptogens have antioxidant properties that can reduce oxidative stress, a key factor in aging and disease development.
4. How to Use Adaptogens
Adaptogens are available in a variety of forms including powders, tinctures, capsules, teas, and sometimes whole foods. The correct dosage may vary depending on the specific adaptogen, individual needs, and health conditions.
- Powder: Can be mixed into smoothies, coffee, or food.
- Capsules: Convenient for daily supplementation.
- Tincture: Concentrated liquid extract that can be added to water or taken directly.
- Tea: Herbs such as holy basil and licorice root are often consumed in tea form for their calming effects.
It is important to cycle the use of adaptogens (e.g., for 6 weeks, followed by a 2-week break) to avoid possible desensitization or loss of efficacy over time.
5. Safety and Side Effects
Although adaptogens are generally considered safe for most people, they should be used with caution in some cases:
- Pregnancy/Breastfeeding: Some adaptogens, such as Ashwagandha, should be avoided during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
- Autoimmune Disorders: Because adaptogens can affect the immune system, people with autoimmune diseases should consult a healthcare professional before using them.
- Drug Interactions: Some adaptogens may interfere with medications, especially those that affect blood pressure, blood sugar, or mental health.
- Dosage: It is important to start with small doses to assess individual tolerance and consult a healthcare professional for guidance.
6. Scientific Research
Scientific studies on adaptogens continue, and while traditional medicine has long supported their use, clinical studies in humans are still limited. However, some research has shown promising results in terms of stress reduction, cognitive enhancement, and immune modulation, especially for herbs such as ashwagandha and rhodiola.
7. Conclusion
Adaptogens offer a natural, holistic approach to improving the body's resistance to stress. By helping the body adapt to physical and mental stress, they promote overall health, energy, and balance. However, as with any supplement, it is important to use them with proper knowledge, taking into account individual health conditions and consulting a healthcare provider when necessary.