Moringa Tea Benefits: Moringa tea is good for what?
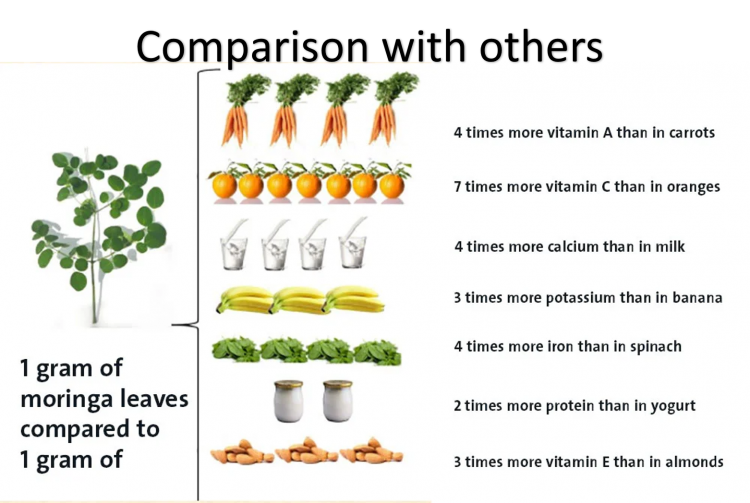
Table of Contents
Moringa tea Benefits and making: 1
Method-1:- A simple cup of moringa tea: 1
How to make Moringa Tea:
Method-1:- A simple cup of moringa tea:

Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon moringa powder (or few dried leaves)
- 8 ounces of water (a cup of water)
- (Optional) Honey, lemon, or another sweetener
Instructions:
- Heat the water: Bring the water to near boiling (about 160°F to 180°F or 70°C to 80°C). You can use a caldron on the oven.
- Steep moringa: If using powder, place 1 teaspoon in your cup. If using leaves, you can place them loosely in a cup or use a tea infuser/strainer. Pour hot water over moringa.
- Let it steep: Cover the cup and let it steep for 5 to 10 minutes. Longer standing can make the flavor stronger.
- Strain (optional): If you used loose leaves, remove them through a strainer.
Enjoy! You can drink the tea plain or add lemon, honey or other sweetener to taste.
Suggestions:
You can regulate the quantity of moringa powder or fresh or dry leaves depending on the strength you like.
For iced tea, steep as usual and then refrigerate or add ice.
Moringa tea powder is widely available online or at health food stores. Dried moringa leaves can be hard to find but can sometimes be found at specialty stores.
Type-2:- Cup of moringa tea:
Ingredients:
- 1 teaspoon moringa powder (or few dried leaves)
- Ginger Root (a small piece)
- 8 ounces of water (a cup of water)
- (Optional) Honey, lemon, or another sweetener

How to Make it:
- Heat the water: Bring the water to near boiling (about 160°F to 180°F or 70°C to 80°C). You can use a caldron on the oven.
- Ginger: Add a small pice of Ginger Root
- Steep moringa: If using powder, place 1 teaspoon in your cup. If using leaves, you can place them loosely in a cup or use a tea infuser/strainer. Pour hot water over moringa.
- Let it steep: Cover the cup and let it steep for 5 to 10 minutes. Longer standing can make the flavor stronger.
- Strain (optional): If you used loose leaves, remove them through a strainer.
Moringa tea Benefits
Moringa tea, derived from the leaves of the Moringa oleifera tree, is celebrated for its numerous health benefits. Here's a detailed summary of the benefits associated with consuming Moringa tea:
Rich in Nutrients:
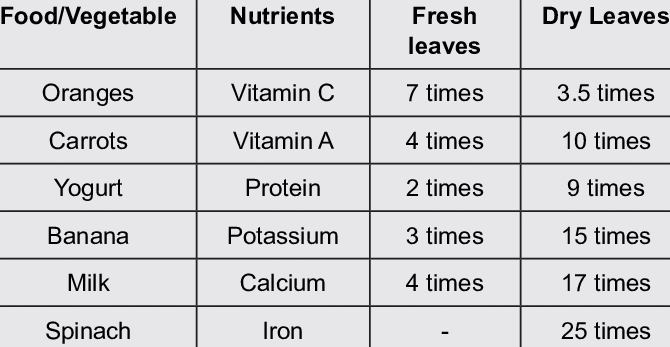
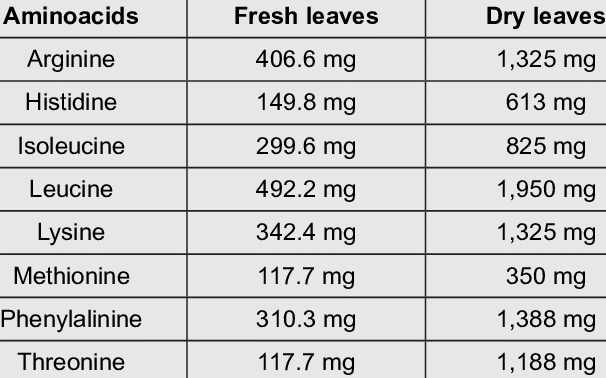
Moringa leaves are filled with vital nutrients, with vitamins (such as vitamin E, C, and A), reserves (like calcium, potassium, and iron), and amino acids. These nutrients subsidize to general health and security.
Antioxidant Properties:
Moringa tea contains powerful antioxidants, such as quercetin, chlorogenic acid, and beta-carotene. These antioxidants help neutralize free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and lowering the risk of chronic diseases.
Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Compounds found in Moringa tea, such as isothiocyanates, have been shown to possess anti-inflammatory properties. Regular consumption of Moringa tea may help alleviate inflammation in the body, reducing the risk of inflammatory conditions like arthritis and promoting overall joint health.
Supports Heart Health:
Moringa tea may contribute to cardiovascular health by lowering cholesterol levels and reducing blood pressure. The antioxidants present in Moringa tea help prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, thus reducing the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
Boosts Immune System:
The abundance of vitamins and minerals in Moringa tea strengthens the immune system, helping the body fight off infections and illnesses more effectively. Regular consumption of Moringa tea may enhance immune function and promote overall health.
Aids Digestion:
Moringa tea is known to support digestive health by promoting regularity, alleviating constipation, and soothing gastrointestinal discomfort. The high fiber content of Moringa leaves aids in digestion and helps maintain a healthy digestive system.
Increases Energy Levels:
Moringa tea is often touted for its energizing properties. The nutrients and antioxidants in Moringa help combat fatigue and increase energy levels naturally, making it a popular choice for those seeking a natural energy boost without the jitters associated with caffeine.
Promotes Weight Loss:
Some studies suggest that Moringa tea may aid in weight loss and weight management. Its ability to enhance metabolism and promote satiety can help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise.
Supports Brain Health:
The antioxidants and neuroprotective properties of Moringa tea may have positive effects on brain health. Regular consumption may help protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and improve cognitive function.
Detoxifies the Body:
Moringa tea acts as a natural detoxifier, helping to cleanse the body of toxins and impurities. Its diuretic properties promote the elimination of waste through urine, supporting the health of the kidneys and liver.
Blood Sugar Regulation:
Early studies suggest moringa may help regulate blood sugar levels, potentially beneficial for diabetics.
Digestive Health: Moringa extracts might help with stomach ulcers, constipation, and some bacterial infections
Overall, incorporating Moringa tea into your daily routine can provide a wide range of health benefits, from boosting immunity and energy levels to supporting heart and brain health. As with any herbal remedy, it's essential to consult with a healthcare professional before adding Moringa tea to your diet, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications.
Related Topic:
What are the side effects of taking moringa leaf powder? By Nutrition Professionals
Moringa for blood sugar: How to control blood sugar with Moringa.
Moringa Tea Benefits: Moringa tea is good for what?
Moringa oil and Moringa tree Powder benefits: Moringa Power
How to control blood sugar with moringa? Moringa Power
More benifits of Moringa Tea
- General well-being. Antioxidants,
- Anti-inflammatory,
- Heart health,
- Immune system,
- Digestive health,
- Energy boost,
- Weight loss aid,
- Brain health,
- Detoxification,
- Nutrient-rich,
- Vitamins,
- Minerals,
- Amino acids,
- Quercetin,
- Chlorogenic acid,
- Beta-carotene,
- Lower cholesterol,
- Blood pressure regulation,
- Anti-fatigue,
- Metabolism boost,
- Satiety,
- Cognitive function,
- Neuroprotection,
- Diuretic,
- Kidney health,
- Liver health,
- Cleansing,
- Herbal remedy,
- Natural energy,
- Anti-aging,
- Skin health,
- Hair health,
- Bone health,
- Muscle health,
- Joint health,
- Anti-arthritis,
- Anti-cancer properties,
- Antimicrobial,
- Antifungal,
- Antiviral,
- Respiratory health,
- Asthma relief,
- Allergy relief,
- Blood sugar regulation,
- Insulin sensitivity,
- Hormonal balance,
- Menstrual health,
- Pregnancy support,
- Postpartum recovery,
- General well-being.
- Rich in nutrients,
- Antioxidant properties,
- Anti-inflammatory effects,
- Supports heart health,
- Boosts immune system,
- Aids digestion,
- Increases energy levels,
- Promotes weight loss,
- Supports brain health,
- Detoxifies the body,
- Enhances metabolism,
- Improves cognitive function,
- Balances cholesterol levels,
- Regulates blood sugar levels,
- Alleviates constipation,
- Soothes gastrointestinal discomfort,
- Protects against oxidative stress,
- Fights free radicals,
- Reduces inflammation,
- Strengthens bones,
- Improves skin health,
- Promotes hair growth,
- Supports liver function,
- Enhances mood,
- Relieves stress,
- Improves sleep quality,
- Boosts overall well-being,
- Enhances athletic performance,
- Improves focus and concentration,
- Regulates blood pressure,
- Fights allergies,
- Reduces the risk of cancer,
- Supports healthy aging,
- Promotes detoxification,
- Enhances nutrient absorption,
- Fights fatigue,
- Supports weight management,
- Boosts metabolism,
- Reduces bloating,
- Alleviates menstrual cramps,
- Supports hormonal balance,
- Improves vision,
- Enhances lung function,
- Fights respiratory infections,
- Reduces the risk of asthma,
- Promotes wound healing,
- Boosts collagen production,
- Improves oral health,
- Fights bacteria and viruses,
- Reduces the risk of infection,
- Supports kidney health,
- Enhances detoxification pathways,
- Improves joint health,
- Reduces the risk of arthritis,
- Supports muscle recovery,
- Boosts endurance,
- Improves flexibility,
- Reduces muscle soreness,
- Supports cartilage health,
- Enhances bone density,
- Reduces the risk of osteoporosis,
- Supports cardiovascular function,
- Improves circulation,
- Reduces the risk of stroke,
- Supports healthy blood vessels,
- Enhances endothelial function,
- Reduces blood clot formation,
- Supports brain function,
- Enhances memory,
- Improves cognitive flexibility,
- Reduces the risk of dementia,
- Supports neurotransmitter balance,
- Enhances neuroplasticity,
- Reduces neuroinflammation,
- Supports mood regulation,
- Enhances serotonin production,
- Improves dopamine sensitivity,
- Reduces anxiety and depression,
- Supports stress management,
- Enhances resilience,
- Reduces cortisol levels,
- Supports adrenal health,
- Enhances thyroid function,
- Reduces the risk of thyroid disorders,
- Supports hormone production,
- Enhances reproductive health,
- Reduces the risk of infertility,
- Supports menstrual regularity,
- Enhances libido,
- Reduces the risk of erectile dysfunction,
- Supports prostate health,
- Enhances sperm quality,
- Reduces the risk of prostate cancer,
- Supports urinary health,
- Enhances bladder function,
- Reduces the risk of urinary tract infections,
- Supports liver detoxification,
- Enhances bile production,
- Reduces liver inflammation,
- Supports liver regeneration,
- Enhances liver function,
- Reduces the risk of fatty liver disease,
- Supports gallbladder health,
- Enhances gallbladder function,
- Reduces the risk of gallstones,
- Supports pancreatic health,
- Enhances pancreatic function,
- Reduces pancreatic inflammation,
- Supports pancreatic enzyme production,
- Enhances digestive health,
- Supports stomach acid production,
- Reduces the risk of gastric ulcers,
- Supports intestinal health,
- Enhances intestinal motility,
- Reduces the risk of constipation,
- Supports colon health,
- Enhances colon function,
- Reduces the risk of colorectal cancer,
- Supports immune function,
- Enhances immune response,
- Reduces the risk of infections,
- Supports lymphatic drainage,
- Enhances lymphocyte function,
- Reduces lymphatic congestion,
- Supports thymus function,
- Enhances T-cell production,
- Reduces autoimmune activity,
- Supports bone marrow function,
- Enhances white blood cell production,
- Reduces inflammation,
- Supports cytokine balance,
- Enhances cytokine regulation,
- Reduces cytokine storm,
- Supports respiratory health,
- Enhances lung function,
- Reduces the risk of respiratory infections,
- Supports bronchial health,
- Enhances bronchodilation,
- Reduces bronchospasms,
- Supports nasal health,
- Enhances nasal mucosa function,
- Reduces nasal congestion,
- Supports sinus health,
- Enhances sinus drainage,
- Reduces sinus inflammation,
- Supports throat health,
- Enhances throat mucosa function,
- Reduces throat irritation,
- Supports ear health,
- Enhances ear drainage,
- Reduces ear inflammation,
- Supports eye health,
- Enhances tear production,
- Reduces eye dryness,
- Supports ocular surface health,
- Enhances corneal function,<