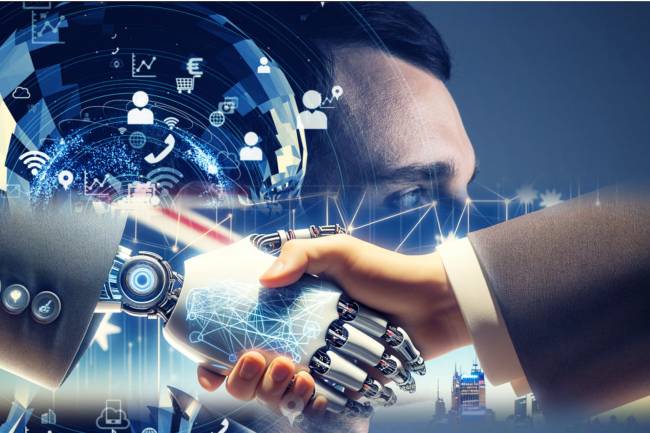
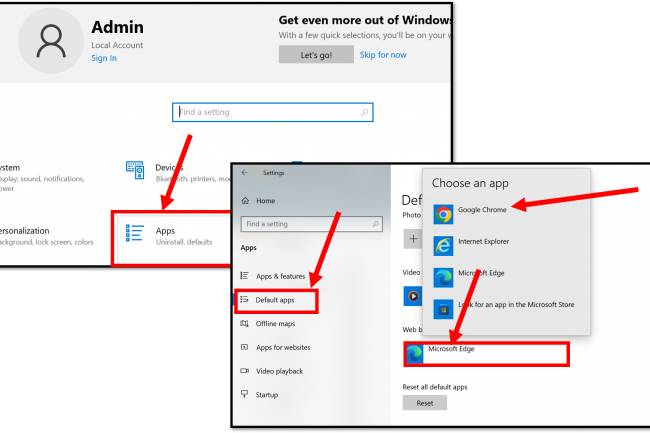
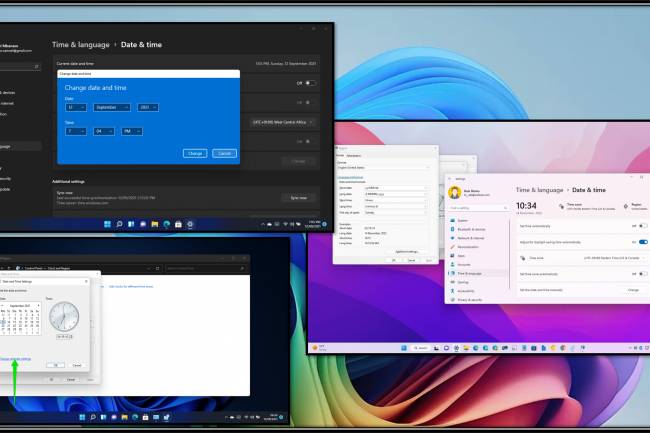
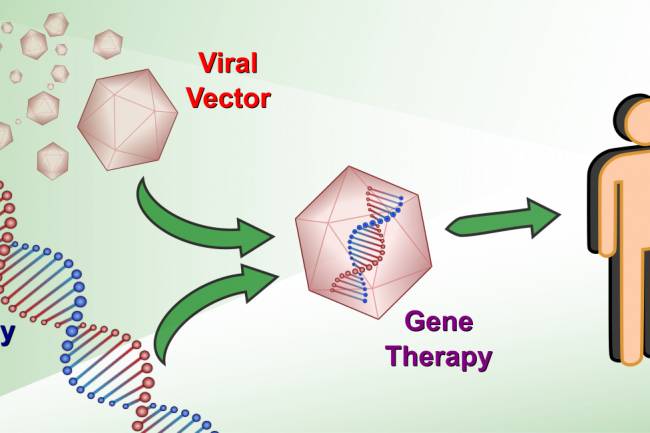
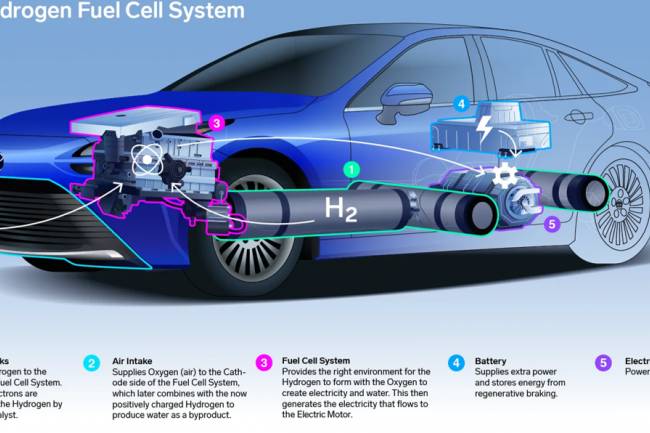
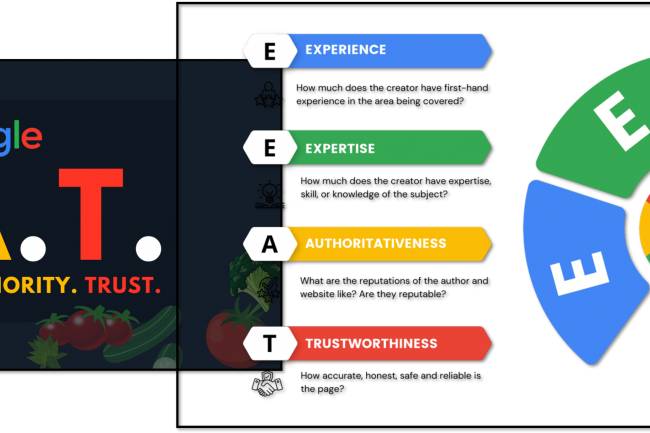
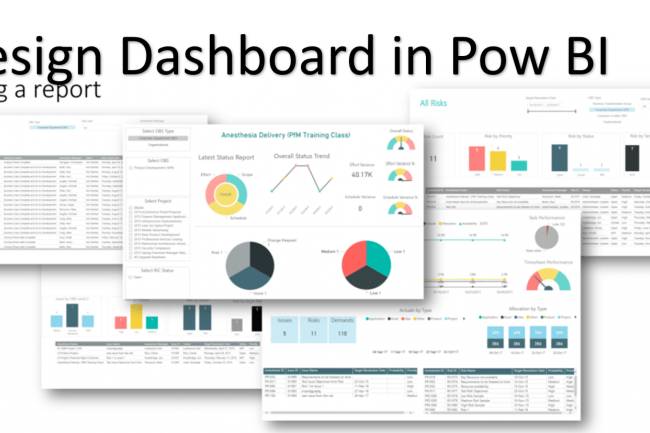
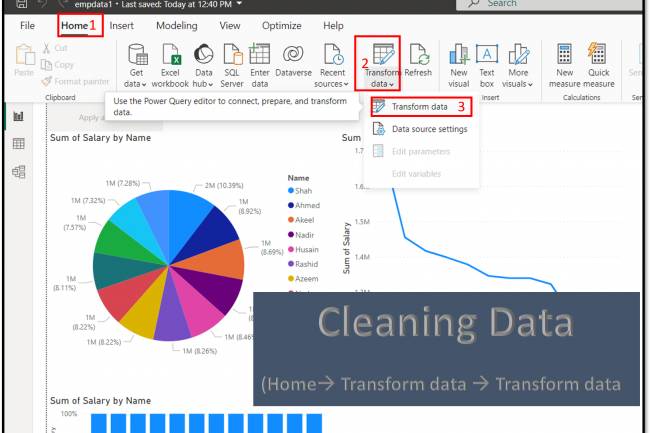
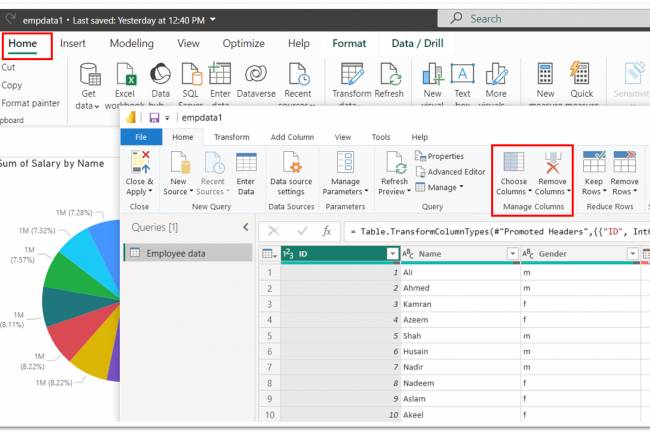
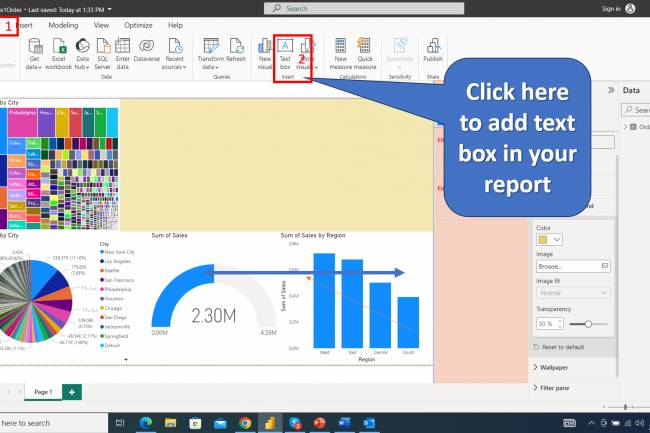
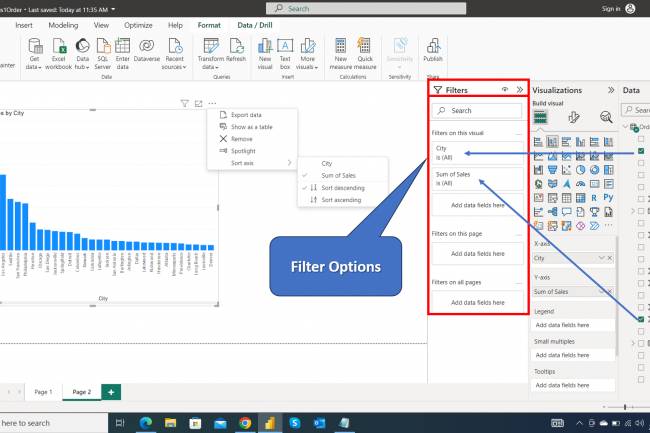
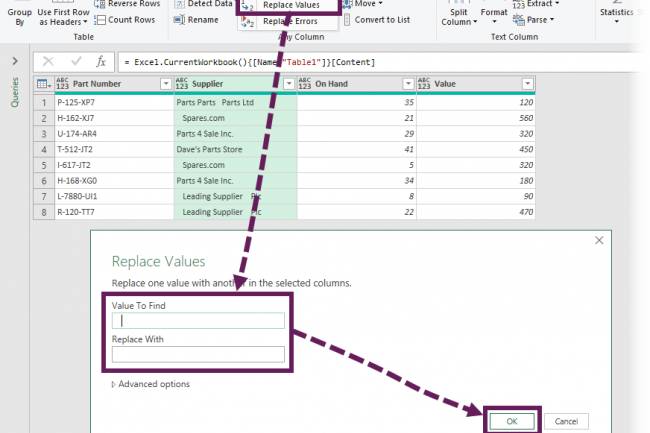
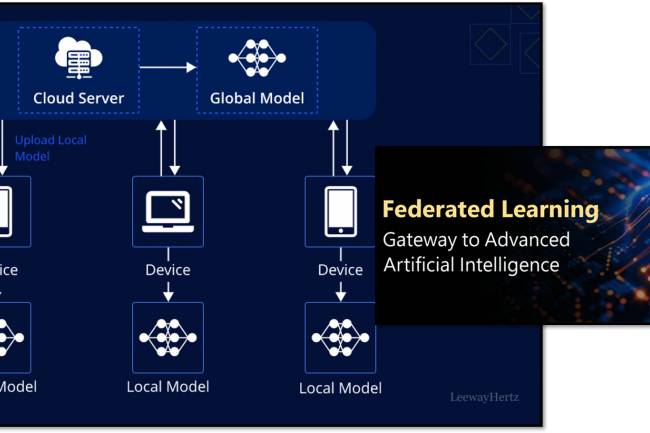
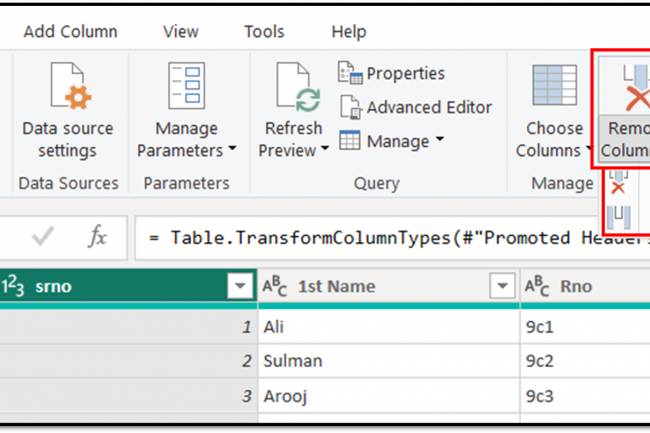
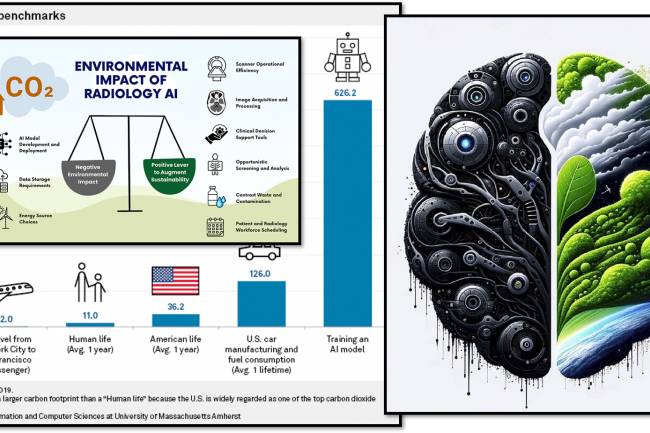
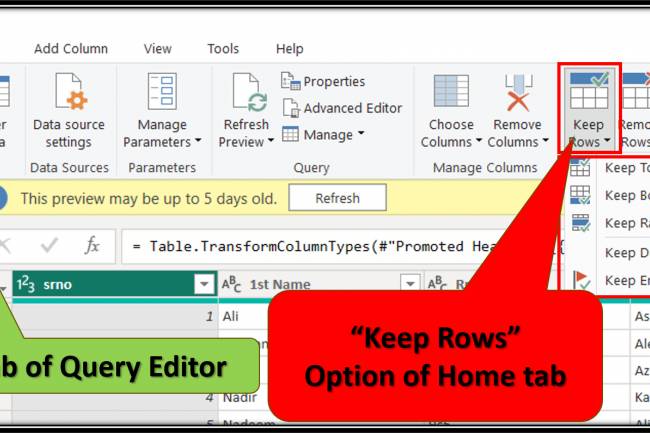
AI amplifies misinformation through deepfakes, bots, and targeted propaganda, making fake news harder to detect.
3D gel nails in pink shades offer textured designs with a glossy or matte finish for a chic and elegant look.
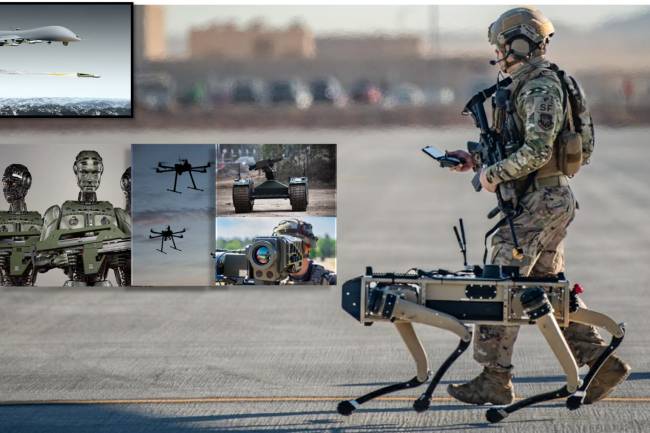
Weaponizing AI provides benefits such as improved combat performance, faster decision-making, and more accurate targeting. However, it has significant drawbacks, including ethical concerns, liability issues, increased risks, and abuse by criminals.
AI automates routine tasks, leading to job displacement in industries such as manufacturing and retail, while creating demand for highly skilled roles in emerging sectors. It increases productivity and innovation but widens income inequality and regional disparities. Adaptation through training, education, and policy reforms is essential to balance economic growth and social equity.
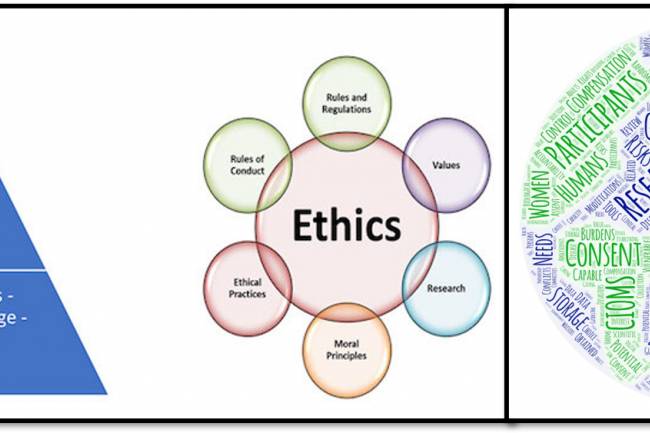
Accountability and transparency in AI ensure that AI systems are ethical, trustworthy, and safe. Accountability includes assigning responsibility for AI decisions, ensuring traceability, conducting audits, and talking harms caused by the technology. Transparency requires making AI processes understandable, disclosing data sources and biases, explaining decision-making, and notifying users when AI is used. Together, these values promote fairness, reduce risks, and build trust in AI systems.
Privacy and Surveillance in the Age of AI explores how AI technologies collect, analyze, and use vast amounts of personal data, often at the expense of individual privacy. Key concerns include mass data collection, facial recognition, predictive analytics, and the risks of re-identification of anonymous data. AI-powered tools are widely used in public surveillance, targeted advertising, and workplace monitoring, exacerbating ethical issues such as bias, discrimination, and lack of transparency. Legal frameworks such as GDPR and CCPA offer some protections, but rapid technological advances often outpace regulations. Strong policies, ethical AI design, and public oversight are needed to strike a balance between reaping the benefits of AI and protecting privacy.